
By BY SIMON ROMERO, RONI CARYN RABIN AND MARK WALKER from NYT Health https://ift.tt/bDB7Srk

Updated COVID vaccines are expected to be available by Labor Day, but public health experts have mixed feelings, with some citing lack of human data and others saying the need is urgent.

Experts warn microwave popcorn could be loading your body with potentially harmful "forever chemicals."

A growing body of research shows that strength training, even in modest amounts, can lower disease risk and add years to your life.
The FDA on Wednesday granted emergency use authorization to Omicron-specific COVID-19 vaccines made by Pfizer/BioNTech and Moderna.
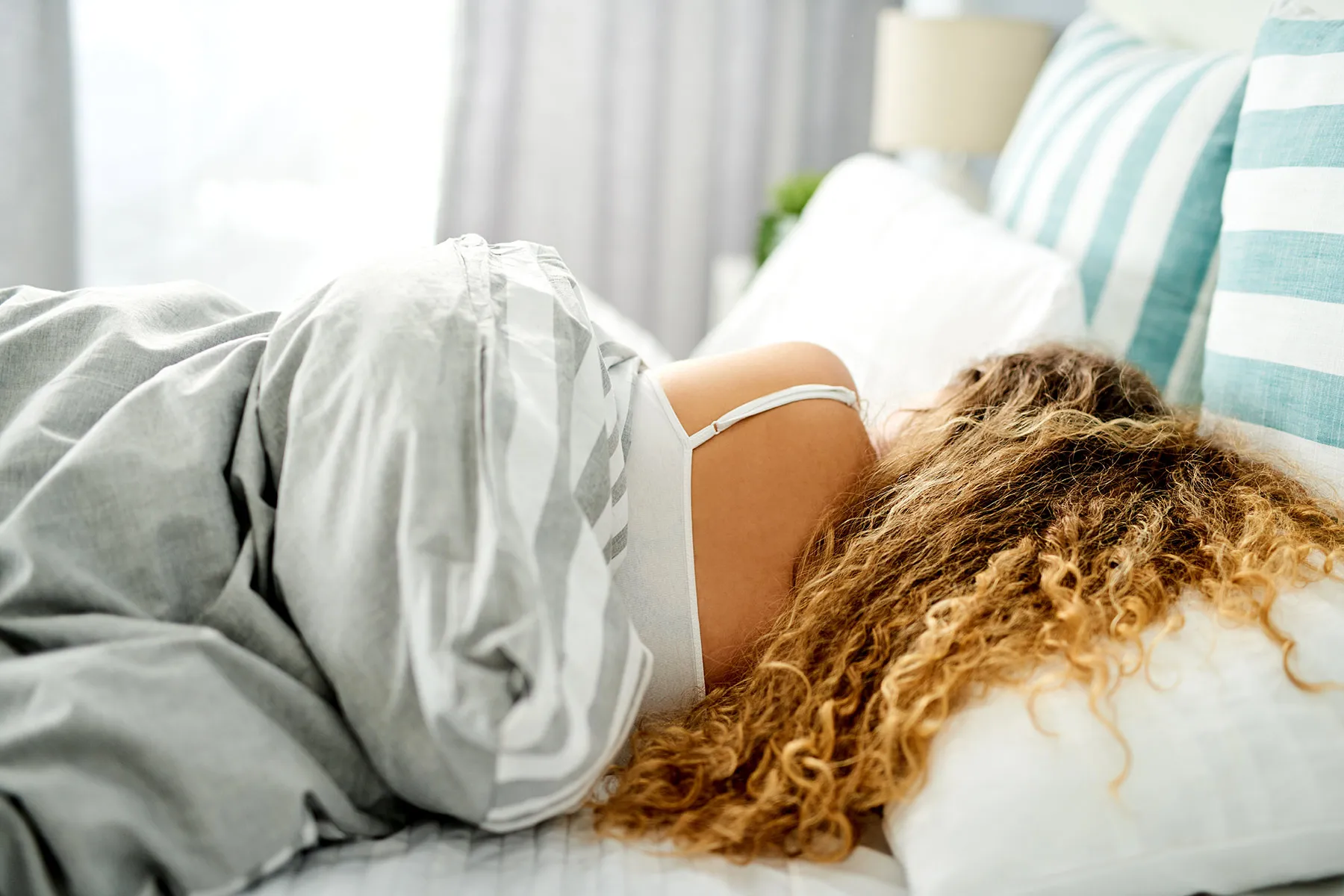


Customers who bought a bestselling mattress sold on Amazon and at retailers nationwide are suing the manufacturer over claims that fiberglass fibers in the product have damaged their health.

From word games to workout challenges to staying sober, tracking a streak has never been easier. How can we leverage that motivational power to keep from being totally derailed when a positive streak, inevitably, ends?
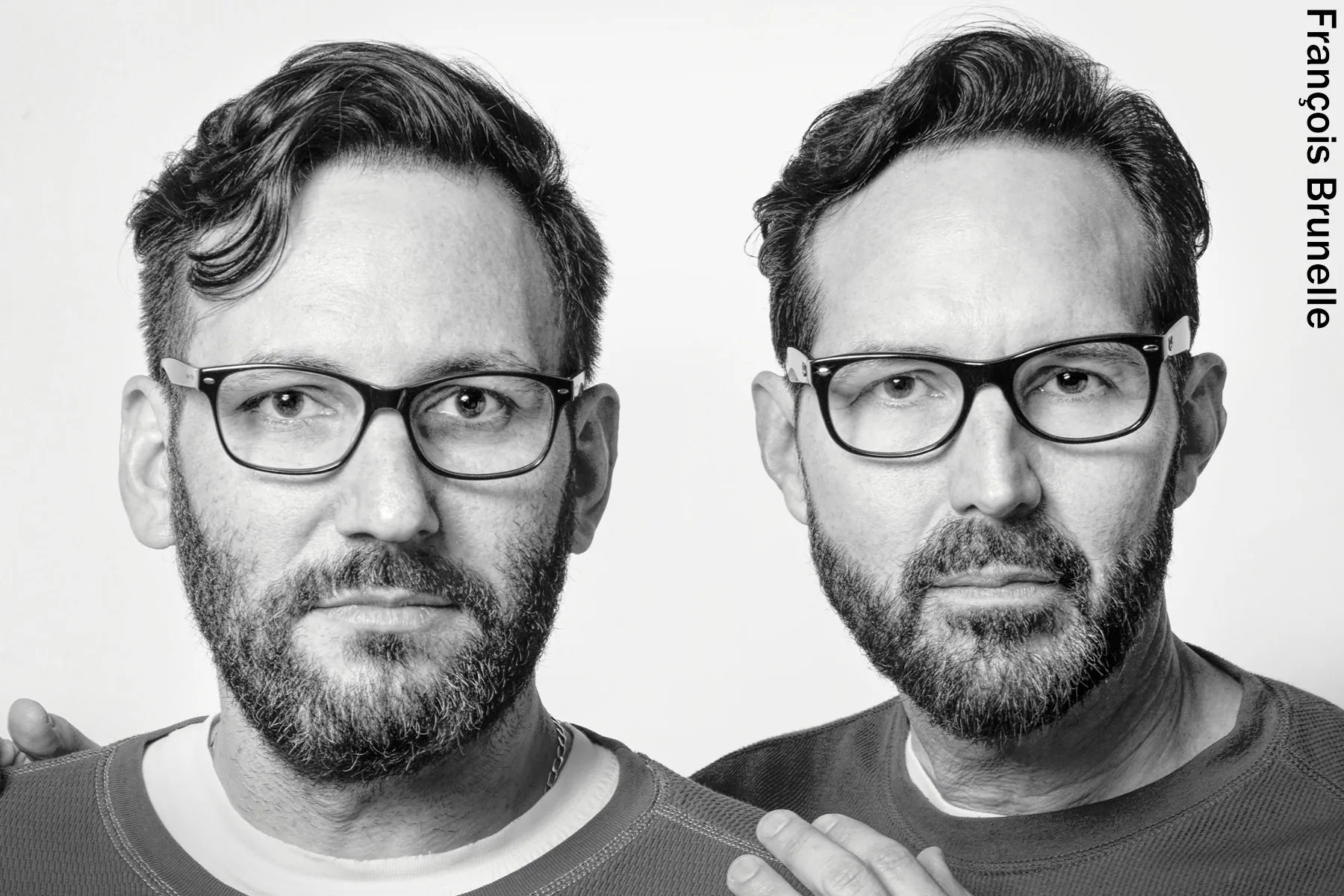


With some doppelgangers, there might be more to the idea than meets the eye. A team of Spanish scientists studied pairs of unrelated look-alikes and found that they not only bear a striking resemblance to each other, but also share significant parts of their DNA.

Bullies' top tactic is social exclusion, also known as "relational aggression." It involves shutting out peers from group activities and spreading false rumors about them.

A new study finds it doesn't seem to matter what time of day or night you take your blood pressure medication.

From fibbing about how much we drink to creating an entire false medical history in plain sight, lying to doctors, colleagues, and loved ones about our health is incredibly common. But why?

Nearly 123,000 cancer deaths – or almost 30% of all cancer deaths – in the United States in 2019 were linked to cigarette smoking, a new analysis suggests.

Labor shortages at Teva Pharmaceuticals have made Adderall hard to find in some drugstores.
New CDC data shows only 10% of the Jynneos vaccine doses have been given to Black people, even though they make up a third of U.S. cases.
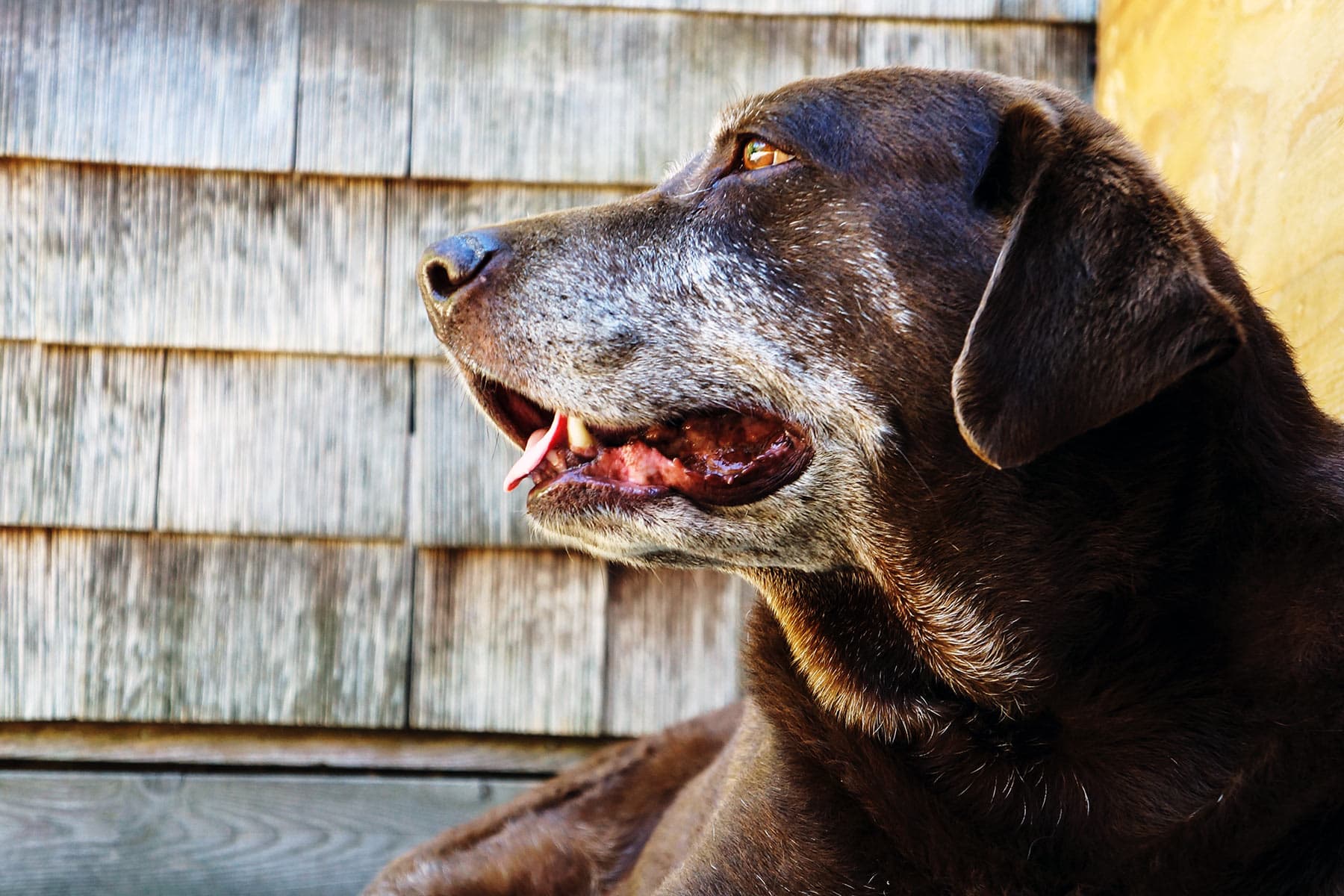



New research shows that risk climbs by half with every extra year of life in a dog's golden years.

Annually, there are an estimated 17,730 new spinal cord injuries in the U.S. and 250,000 to 500,000 worldwide. The U.S. Senate has designated September as National Spinal Cord Injury Awareness Month.
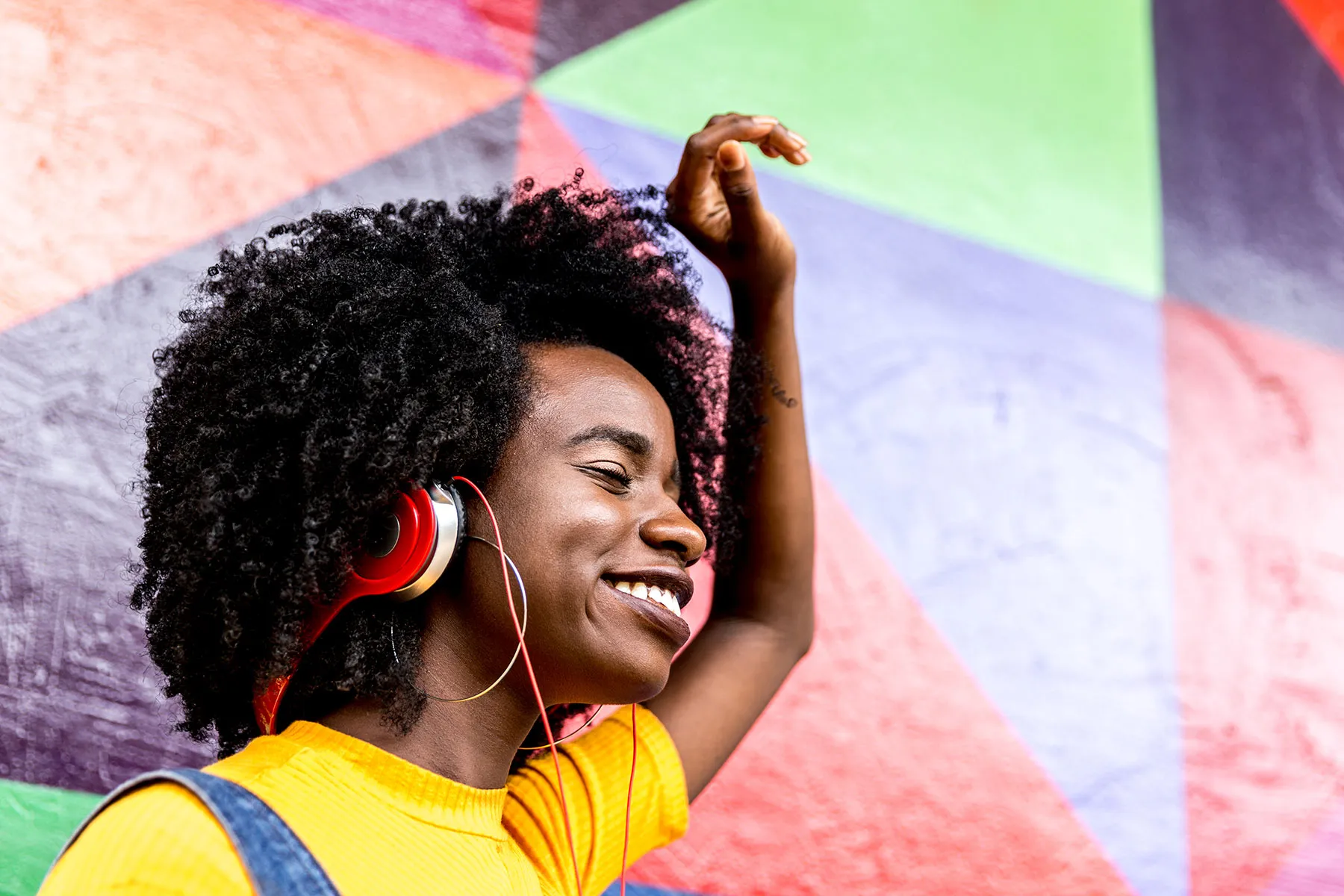

Doctors have long known music and sound can help soothe physical pain, but they didn’t know why. New research offers insight – and a surprise about volume.

Sometimes broken bones fail to fuse together, and understanding why some bones mend while others need more help will improve care for people with fractures.
The exact source of the outbreak has not been officially confirmed, but the CDC said that in 84% of cases people reported eating at Wendy's before they became ill.
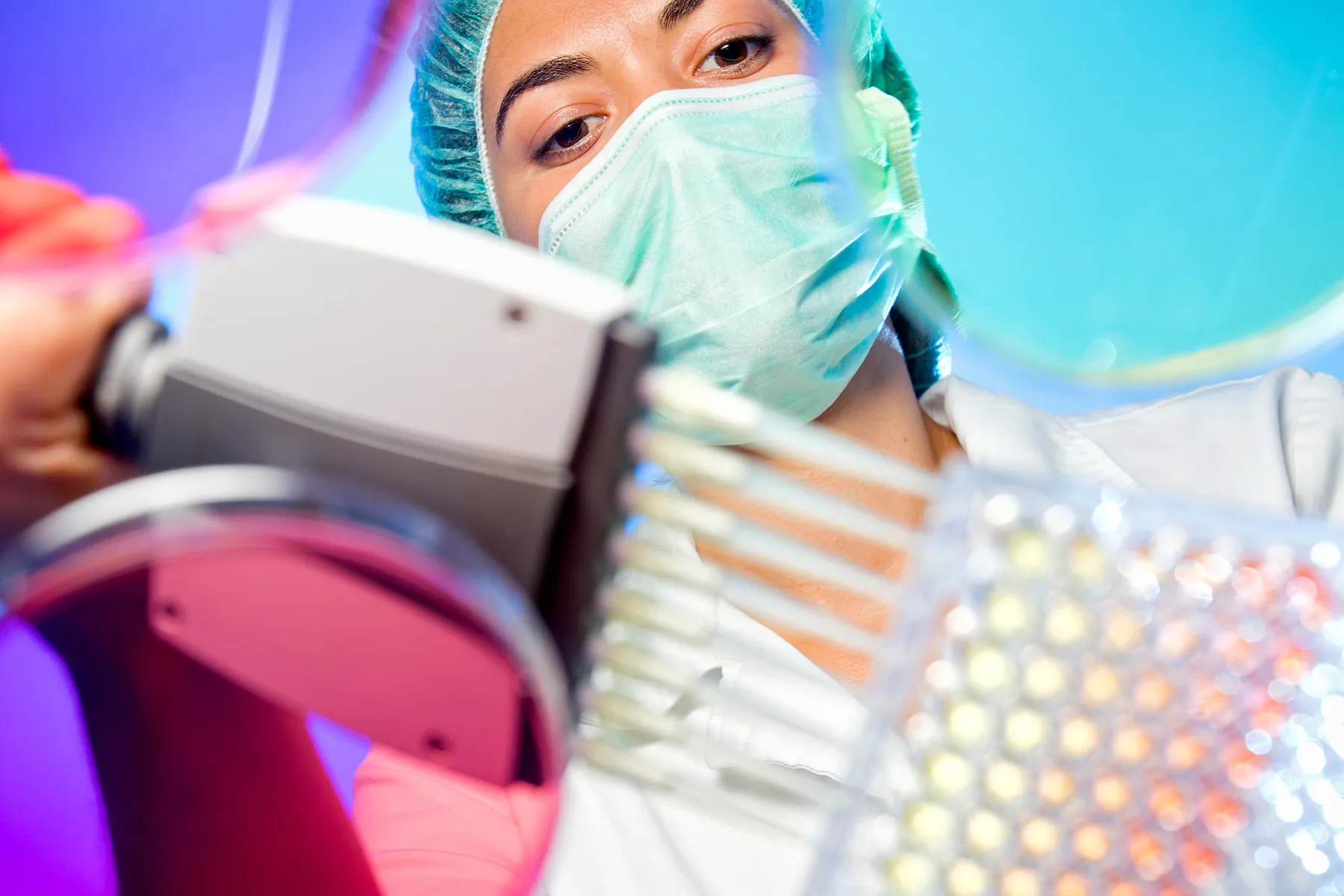


The drug ublituximab beat a standard oral medication for MS in reducing patients' relapses and proved better at preventing areas of inflammatory damage in the brain.
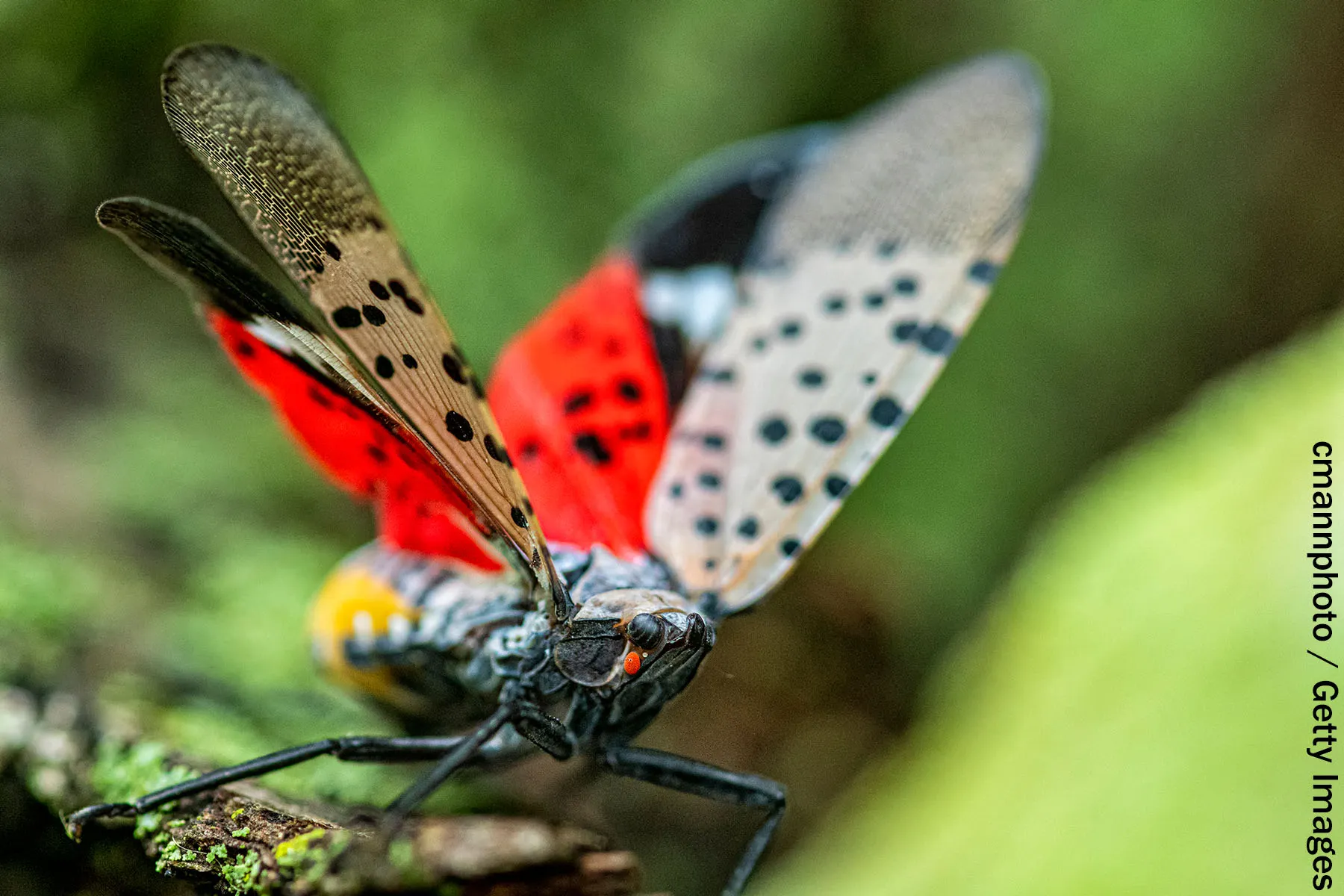


This fast-spreading invasive species damages crops and must be wiped out, agricultural sources say.

Lori McClintock, the wife of U.S. Rep. Tom McClintock of California, died after ingesting white mulberry leaf, according to the Sacramento County coroner. The plant is generally considered safe and is used in herbal remedies that claim to lower blood sugar, boost weight loss, and combat high cholesterol. Her death highlights the potential dangers of dietary supplements.
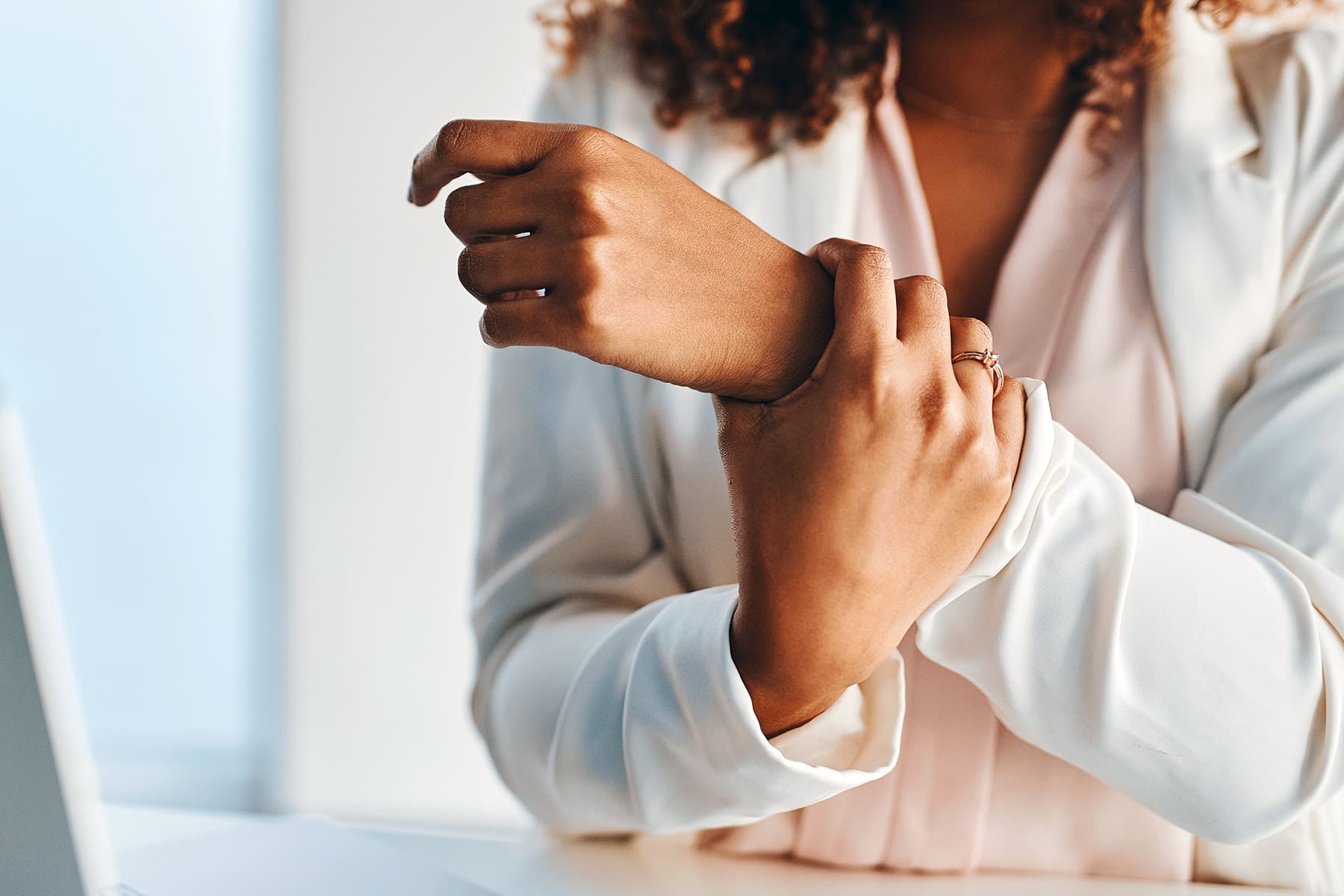


Without the use of any medication, this device under development cools and numbs the nerve sending pain signals to the brain without affecting surrounding nerves or tissue.
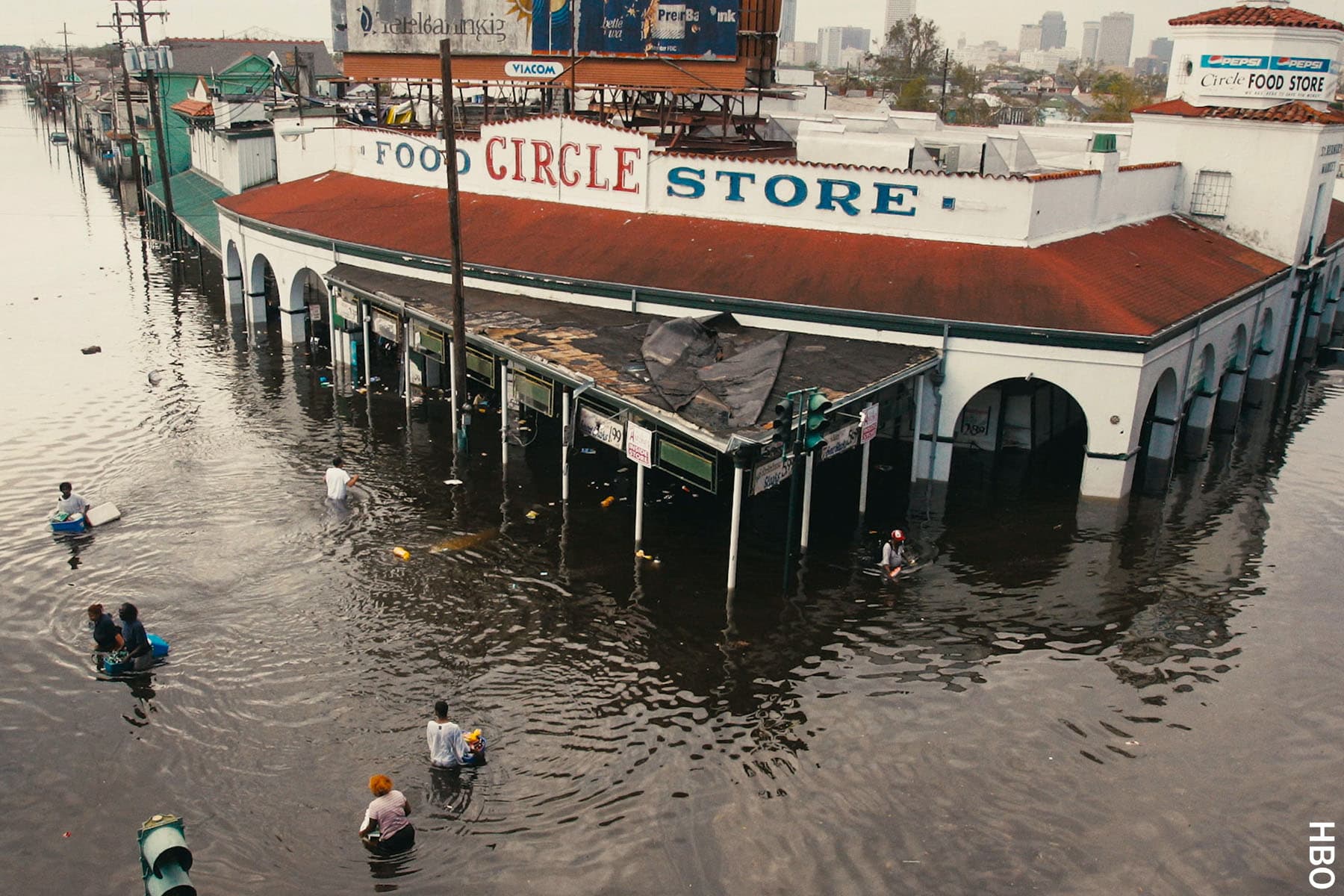

A New Orleans-based filmmaker argues that Black children’s trauma was ignored, and links it to the city’s ongoing struggles with violence
Health authorities are investigating a parvovirus-like illness that has killed more than 30 dogs in northern Michigan, most within three days.
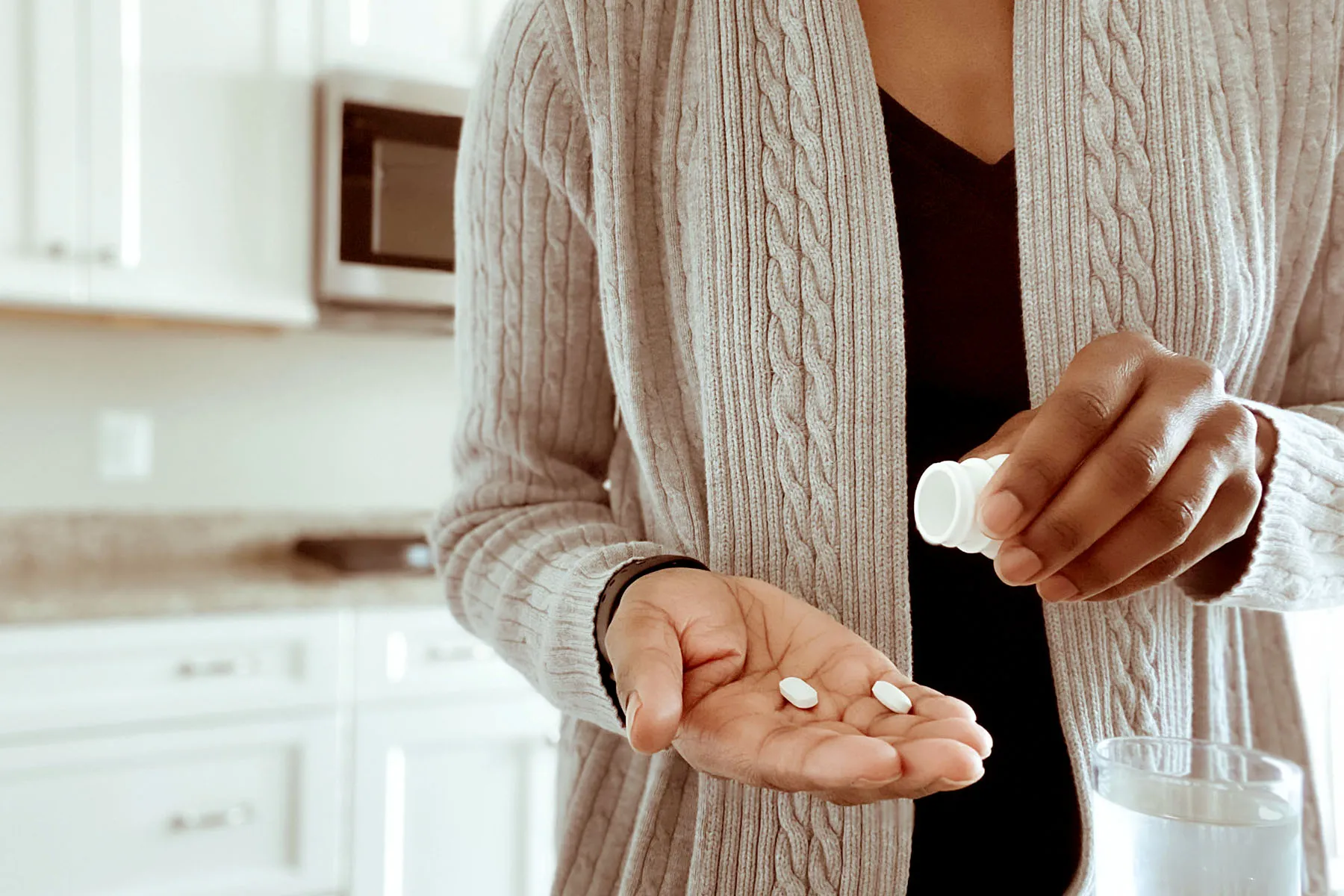

Researchers found use of sleep aids dropped 31% between 2013 and 2018.
The emergence of long COVID was no surprise to researchers who study the post-viral condition myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome, because the same set of symptoms has arisen after many other viruses.
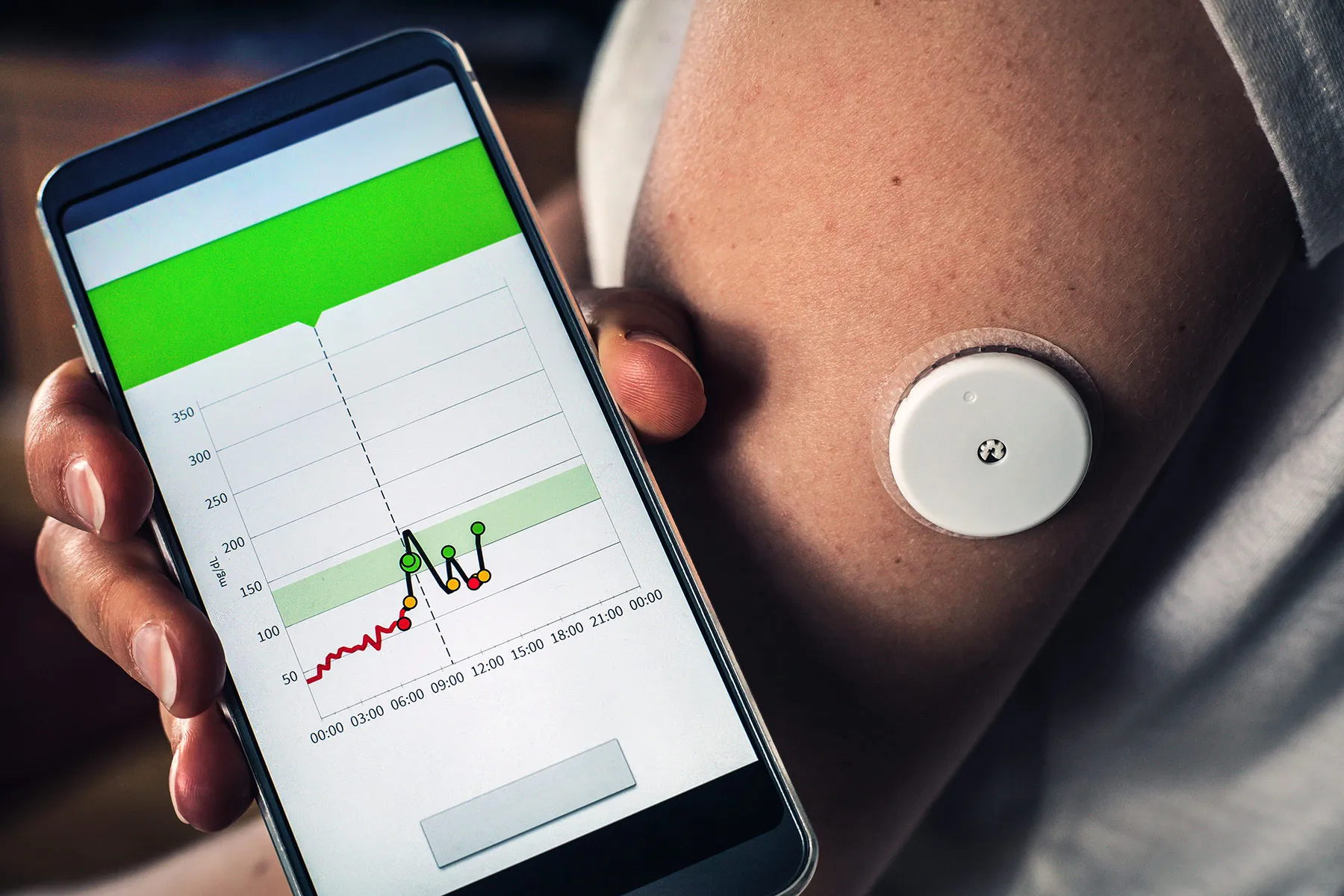
Prepare for a future where you and your doctor track your health markers 24/7, manage chronic conditions in real time, and predict incoming illness with incredible precision – all from tiny sensors you’ll wear on your skin and in your clothing.
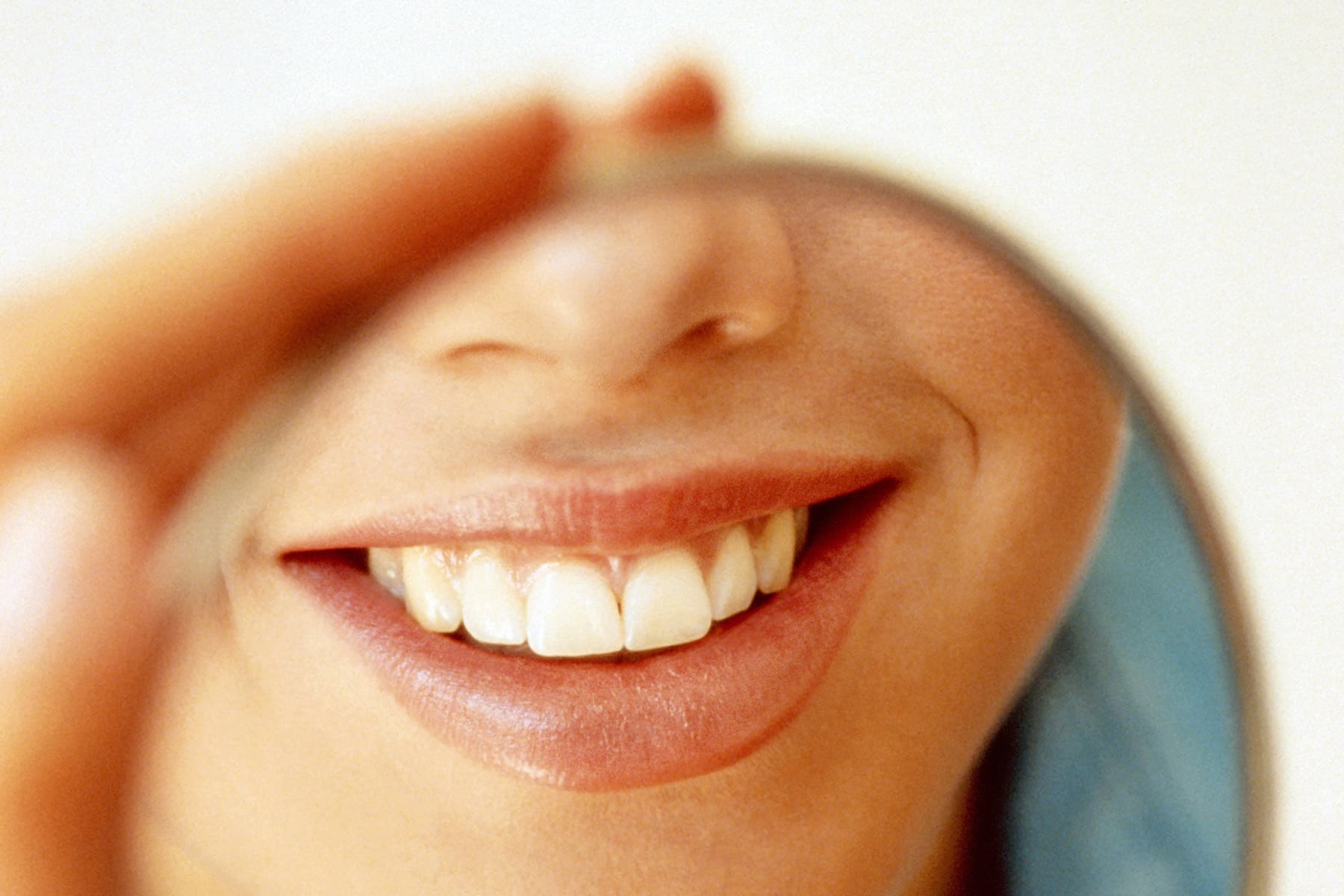


University of Pennsylvania researchers say new technology could be the biggest change to happen to oral care in hundreds of years.

New research estimates that the use of LSD rose from less than 1% in 2002 to 4% in 2019 among people aged 18 to 25.
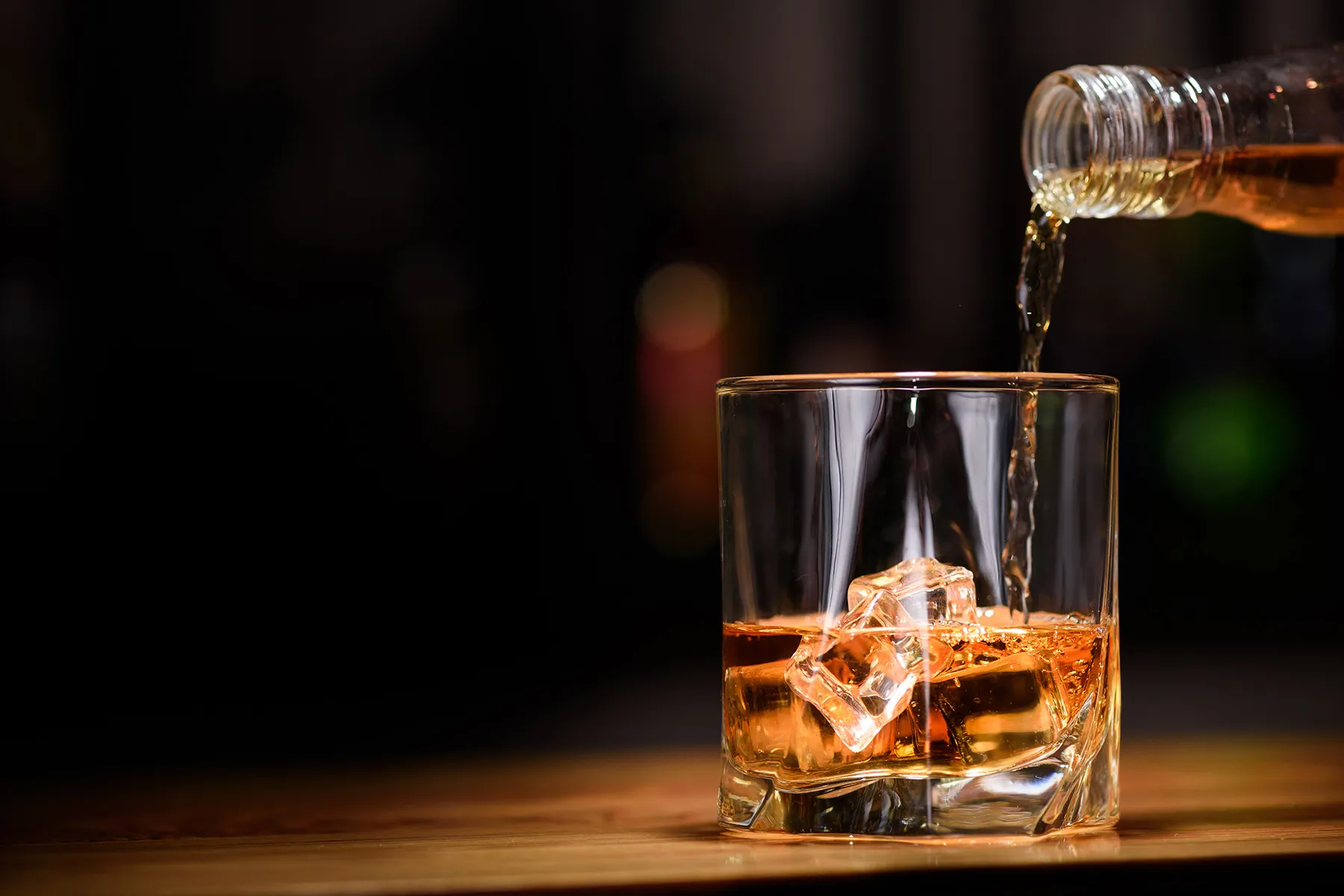

We live in particularly stressful times, and some people turn to alcohol to cope with challenges, from the COVID-19 pandemic to any number of personal stressors. And though self-treating stress with alcohol is not new, there is evidence the pandemic has raised the stakes.
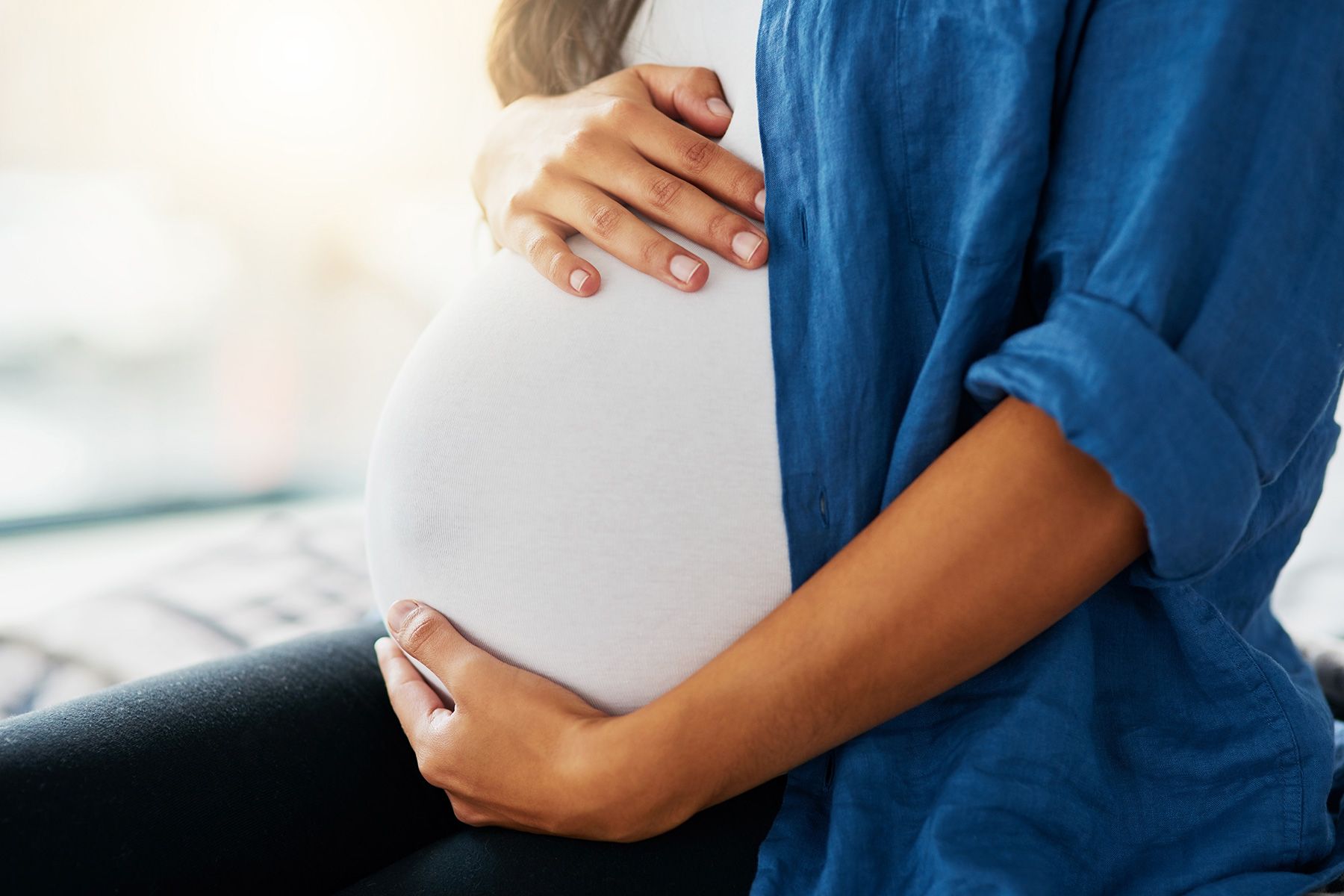

The maternal mortality rate in the U.S. is the highest among industrialized nations. And it’s three times as common among Black women as in white women in the U.S. Here’s what one New York hospital is doing to train doctors to respond.
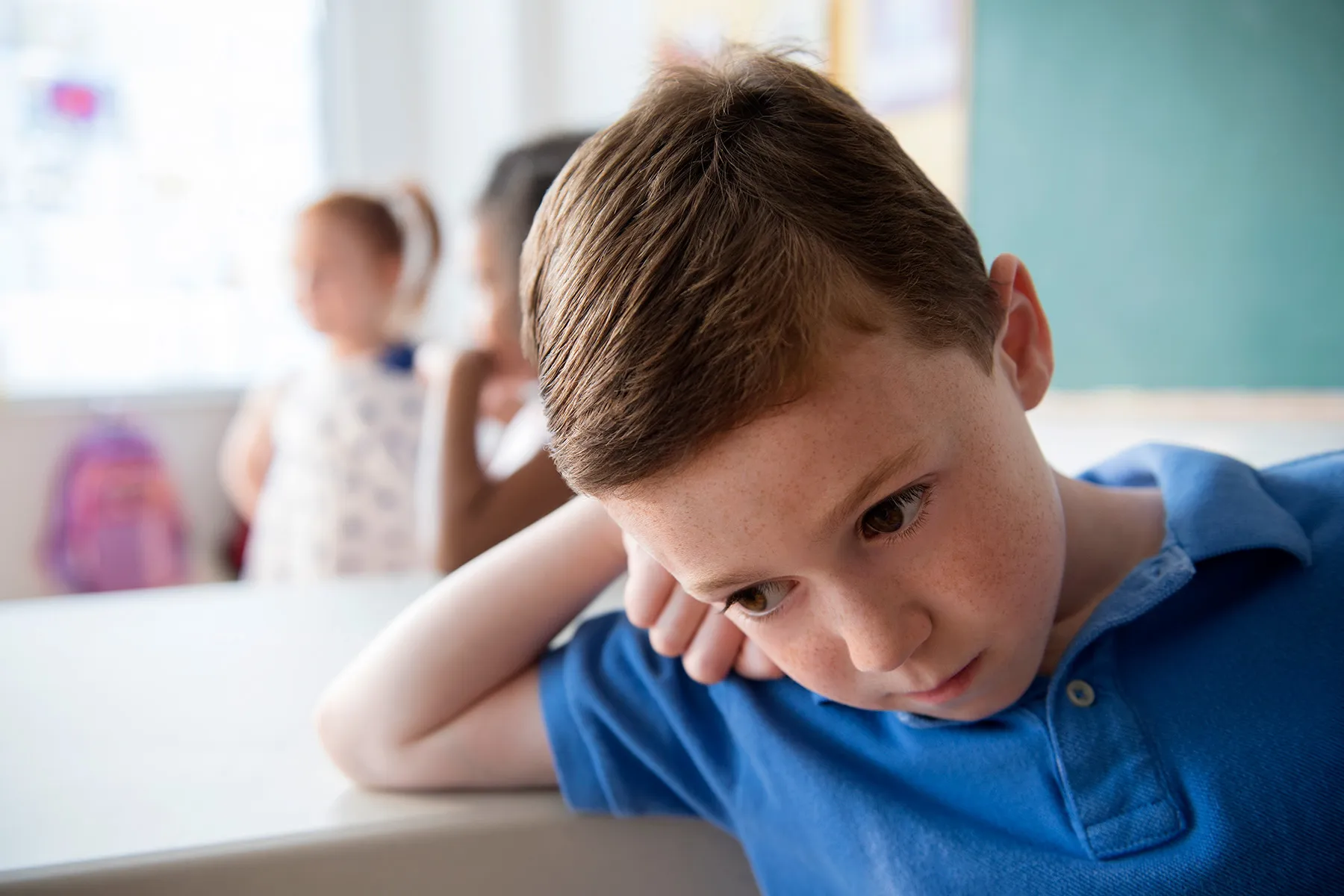

What does it take for a child to be resilient after a major setback? Find out what makes a difference.
Older adults with an upper heart chamber that’s of abnormal size or doesn’t work well may have up to a 35% higher risk for dementia, according to new research.
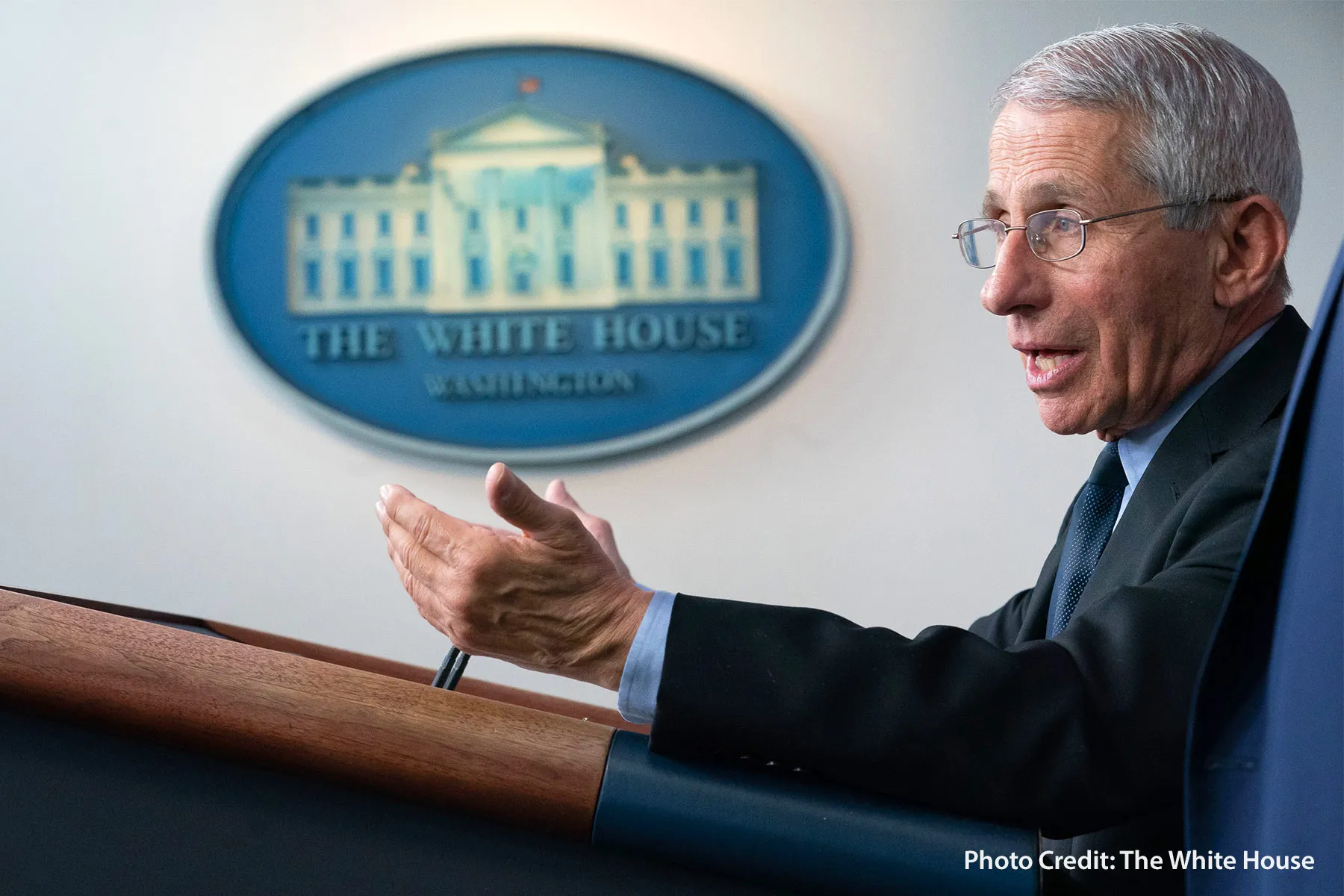

The long-time head of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases will step down in December.
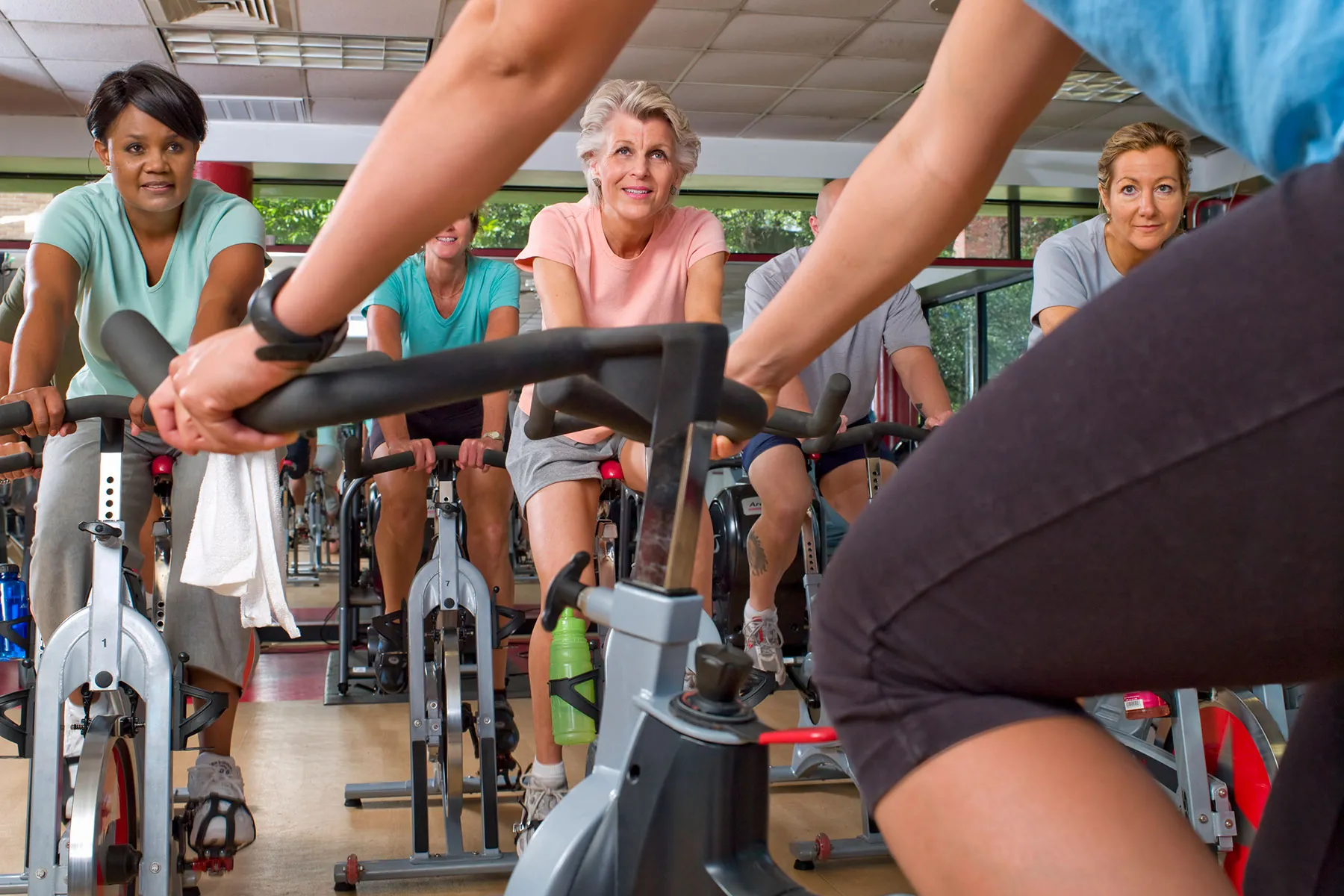

New research suggests there's a category of "diet-resistant" people who need to work out and watch what they eat to lose weight.


A one-year “look-back window” for survivors to file lawsuits against abusers and institutions gives New Yorkers a chance to heal
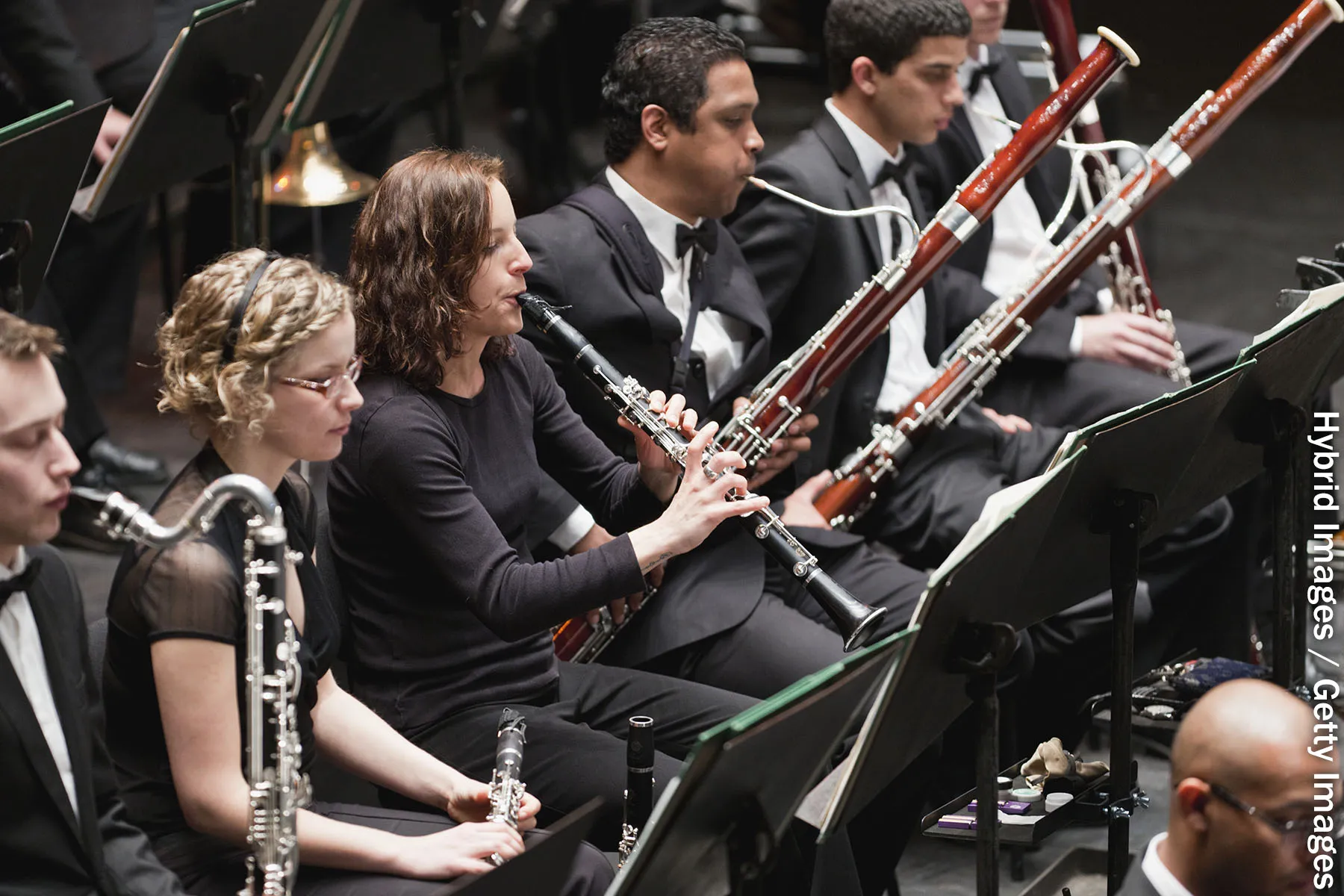

Good news for music lovers and musicians, too: Wind instruments don't appear to project COVID-19 particles more than talking does, according to a new study.
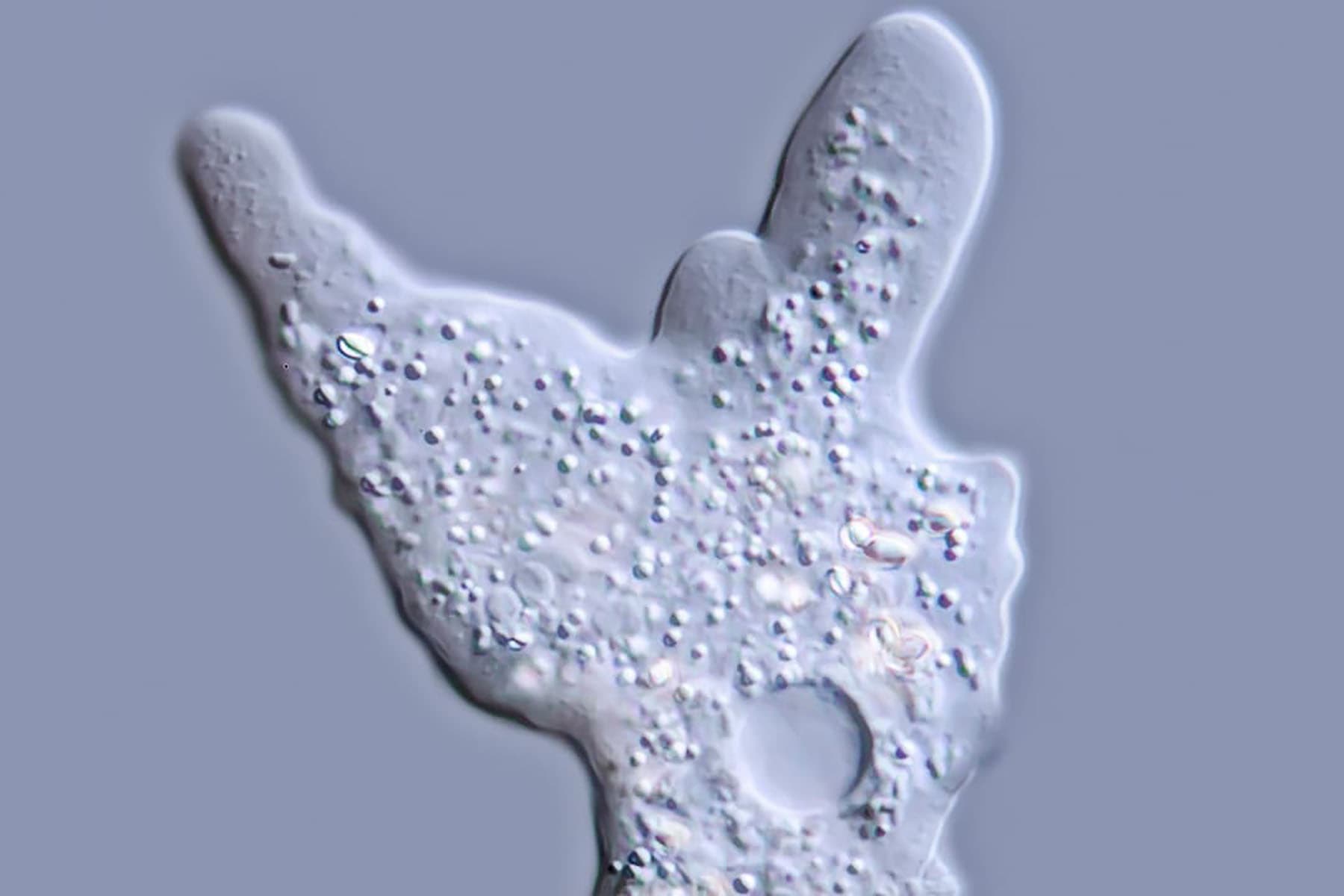
The death of a child in Nebraska was likely caused by an infection with a “brain-eating amoeba” that occurred after the child swam in a local river.